A Vegetation Inventory of the Proposed Eastex Reservoir
Texas Parks and Wildlife Department and Texas Water Development Board
Interagency
Contract No. 93-483-358
October 1993
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to classify, delineate, and map major vegetational communities for the proposed Eastex Reservoir in Cherokee County, Texas. The study was conducted through a Water Research and Planning Grant Operating Agreement (TWDB contract No. 93483-358, TWPD contract No. 333-0214) between the Texas Water Development Board (TWDB) and Texas Parks and Wildlife Department (TPWD). The vegetation mapping and inventory included a multi-temporal data analysis for different years to assess land-use changes. These studies were accomplished through a subcontract (TPWD Interagency Contract No. IAC [92-93] 2174, SWT # 754-C-0033) with the Department of Geography and Planning, Southwest Texas State University. The work was conducted under the supervision of Dr. Ryan Rudnicki. Vegetation inventory data submitted to the TWDB will be used by the Board to evaluate and compare environmental factors associated with proposed reservoir sites in East Texas.
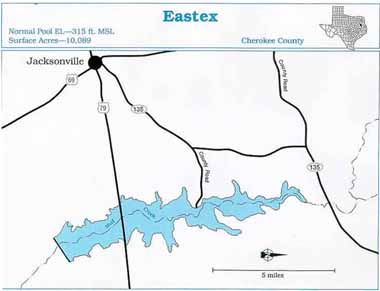
Study Area
The Eastex Reservoir site lies within a portion of the floodplain of Mud Creek in Cherokee County. Mud Creek is within the Neches River Basin. The site is approximately 6 miles east of Jacksonville, Texas (Figure 1). The reservoir will lie within the Pineywoods ecological region (Gould et.al. 1960). Climate can be generalized as subtropical, humid, with warm summers and mild winters. The average annual precipitation ranges between 40 and 44 inches, average annual high temperature ranges between 76 and 77 degrees F., while average annual low temperature ranges between 53 and 55 degrees F. The averageannual gross lake surface evaporation rate for this region is about 50 inches (Texas Department of Water Resources 1983).
Major vegetation cover types typical of this region have been previously mapped (McMahan et. al.1984). These include a mixed pine-hardwood forest interspersed by non-native grasslands and bottomland hardwood communities along creek and river drainages. Commonly occurring plants within the mixed pine-hardwood association include loblolly pine, shortleaf pine, sweetgum, water oak, willow oak, southern red oak, winged elm, American beautyberry, hornbeam, dogwood, and yaupon. Bottomland hardwood areas include water oak, elm, hackberry, southern red oak, white oak, willow, cottonwood, pecan, and dogwood. The study area appears to have been subjected to numerous land-use changes between the early 1980's and 1993. Confirmation of such changes was one of the tasks of this study. Additional descriptions of the study area have been previously documented in a publication entitled "Lake Eastex Regional Water Supply Planning Study" (Lockwood, Andrews & Newnam, Inc. et.al. 1991).
- Gould, F. W., G.O. Hoffman and C.A. Rechenthin. 1960. Vegetational areas of Texas. Tex. A&M Univ. Tex. Agric. Exp. Sta. Leaflet 492.
- Larkin, T.J., and G.W. Bomar. 1983. Climatic atlas of Texas. Tex. Dep. Water Re3s. LP-192, 149p.
- Lockwood, Andrews, and Newnam, Inc. 1991. Lake Eastex regional water supply planning study. Vols 1 &2.
- McMahan, C.A., R.G. Frye and K.L. Brown. 1984. The vegetation types of Texas including cropland. Tex. Parks and Wildl. Dep. Bull. 7000-120. 40p.
- Texas Water Development Board. 1990. Water for Texas-today and tomorrow. Tex. Water Dev. Board Doc. No. GP-5-1.
 (
(