Federal and State Listed Species of Texas:
star cactus
Current
Historic
null
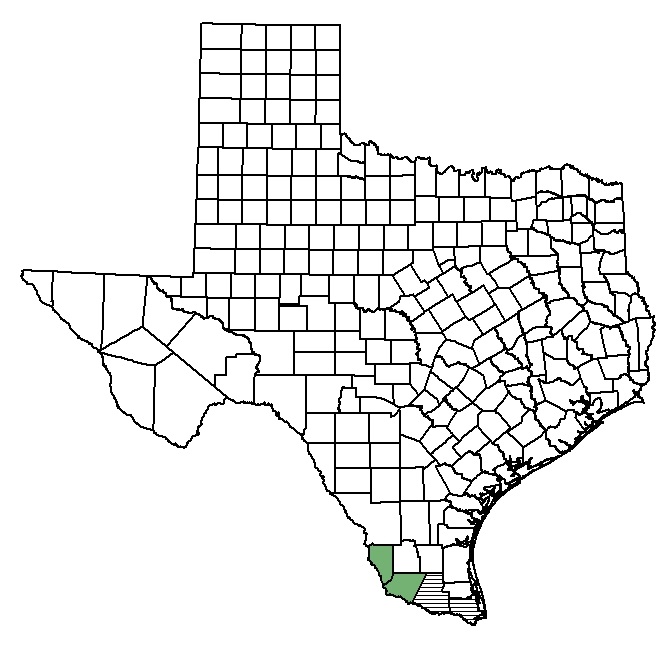
Distribution map of star cactus (Astrophytum asterias).
Global Location
Star cactus occurs in the Rio Grande Valley of South Texas (Starr and Zapata counties, historically in Hidalgo, and reported from Cameron County although no habitat exists there). The cactus also grows in northern Mexico in Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, and Tamaulipas.
null
Credit:
Description
In the wild, star cactus is a flat, or at most, dome-shaped, spineless cactus to 15 cm in diameter. The green or dark-green to brownish green stems are divided into eight triangular sections. Each section has a row of small, white tufts of hairs down its middle. Generally, the stems are also dotted with scattered white specks. Star cactus flowers are yellow with a red to orange center (3-5 cm in diameter). The green, woolly fruits are oval (15-20 mm long, 12 mm wide) and turn brown-red at maturity.
The stems of star cactus very commonly turn color throughout the year possibly due to intense sunlight or water stress.
Credit: Sandy Birnbaum - Texas Parks & Wildlife Dept.
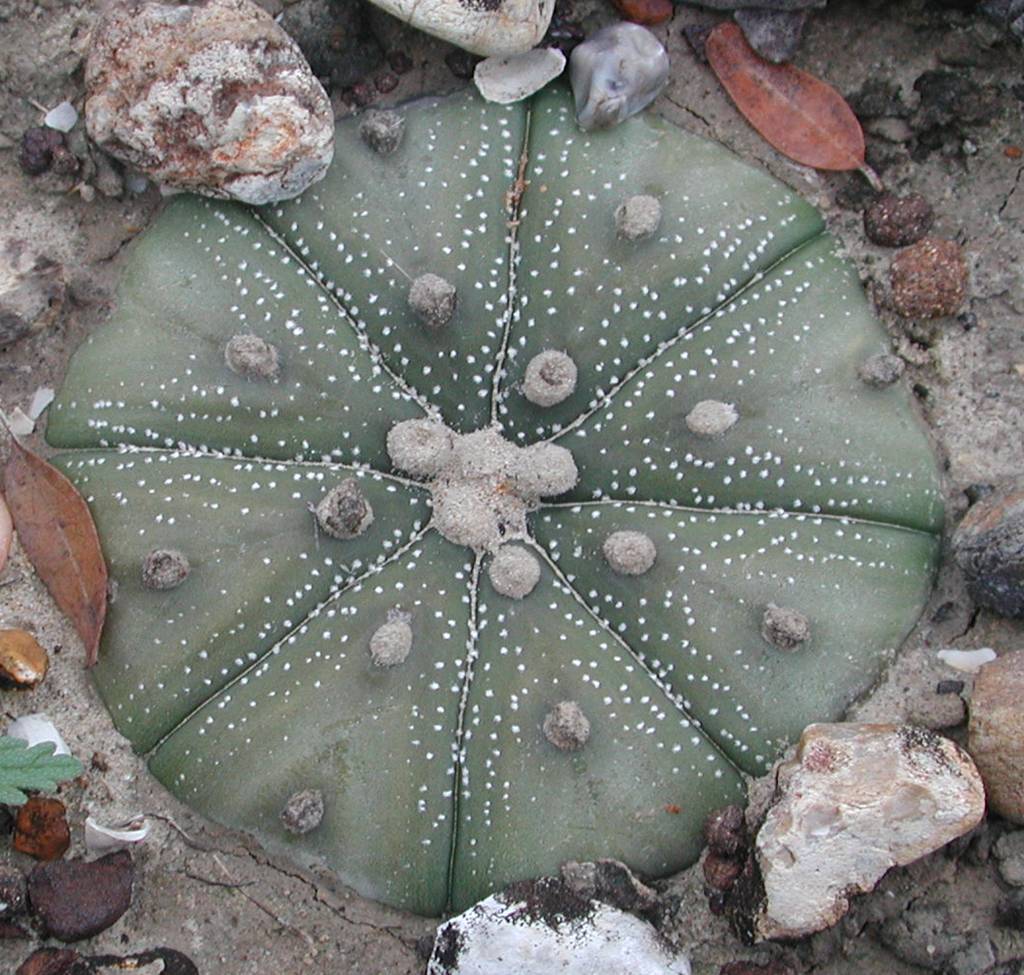

The green/dark-green star cactus stems are divided into 8 sections and have scattered white specks.
Credit: Anna Strong - Texas Parks & Wildlife Department.
The flowers of star cactus are yellow with a red to orange center and 3-5 cm across.
Credit: Sandy Birnbaum - Texas Parks & Wildlife Dept.
Similar Species
Star cactus can be confused with peyote (Lophophora williamsii). The stems of peyote are bluish-green, can have 5-13 variously shaped sections, and have no white specks. Peyote also has pink flowers that are smaller (≤2 cm across) than star cactus flowers.
The bluish-green peyote stems have 5-13 sections and lack white specks. The flowers are pink and less than 2 cm across.
Credit: Anna Strong - Texas Parks & Wildlife Department.
null
Credit:
null
Credit:
null
Credit:
null
Credit:
null
Credit:
Floral Characters
nullLeaf Characters
nullnull
Credit:
null
Credit:
null
Credit:
Habitat
Star cactus grows on gravelly, somewhat salty, clay or loam soils in areas of sparse vegetation in grassy thornscrub.
Habitat of star cactus
Credit: Paula Williamson - Texas State University
Life Cycle Events
Star cactus flowers March through May and occasionally after high rainfall; fruiting follows from April to June.
Survey Season
Star cactus can be identified all year round; however, it is most visible while in flower March to May. During extreme drought, the plants may sink below the ground surface, becoming extremely cryptic and difficult to find.
null
Additional Information
- Rare Plants of Texas
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- NatureServe
- Flora of North America
- Center for Plant Conservation
- Janssen, G.K., J.M Poole, and P.S. Williamson. 2010. The research and recovery of star cactus (Astrophytum asterias). Section 6 final report. Austin: Texas Parks & Wildlife Department.
- Westlund, B.L. 1991. Cactus trade and collection impact study. Section 6 final report. Austin: Texas Parks & Wildlife Department.
Comments
First collected from the wild in the mid-1800s, star cactus is now widely available for sale among cactus growers. In fact, it may be that over-collection in the last 150 years adds to its scarcity. However, its cryptic nature may decrease the possibility of collection. Occurring flush to the ground, star cactus can easily disappear under soil and leaf litter.