Chihuahuan Loamy Plains Desert Grassland
Geology
Primarily occurs on Quaternary alluvium. Included in this system are also grasslands that occupy other formation at higher elevations of mountain foothills. These grasslands may occupy various sedimentary and igneous substrates.
Landform
Level intermountain basins as well as level to gently rolling landforms on the foothills.
Soils
Loamy soils. The foothill grasslands often occupy Shallow Ecological Sites over Perdiz Conglomerate, but may also occur on gravelly sites.
Parent Description
Currently this system (as considered for Phase 5) includes two somewhat distinct grassland types. These grasslands occupy loams of the intermountain basins, and also represent foothill grasslands that occupy shallow soils at the basin edges. These types are often closely juxtaposed and share graminoid composition but differ in abiotic sites, aspect, and invading shrubs. The loamy grasslands are dominated by species such as Bouteloua gracilis (blue grama), Bouteloua curtipendula (sideoats grama), Bouteloua eriopoda (black grama), Pleuraphis mutica (tobosa), Scleropogon brevifolius (burrograss), Bothriochloa laguroides ssp. torreyana (silver bluestem), Bothriochloa barbinodis (cane bluestem), and Dasyochloa pulchella (fluffgrass). These grasslands occur in extensive level plains with deep soils. Prosopis glandulosa (honey mesquite) is the common shrub invader. Other shrubs present to dominant as invaders include Larrea tridentata (creosotebush), Flourensia cernua (tarbush), and Mimosa aculeaticarpa var. biuncifera (catclaw). The foothill grasslands are of similar composition with respect to grasses, but occupy rolling landscapes at slightly higher elevations and are on shallow soils. Condalia ericoides (javelina bush), Juniperus spp. (junipers), and Acacia constricta (whitethorn acacia) are common invaders.
Ecological Mapping Systems
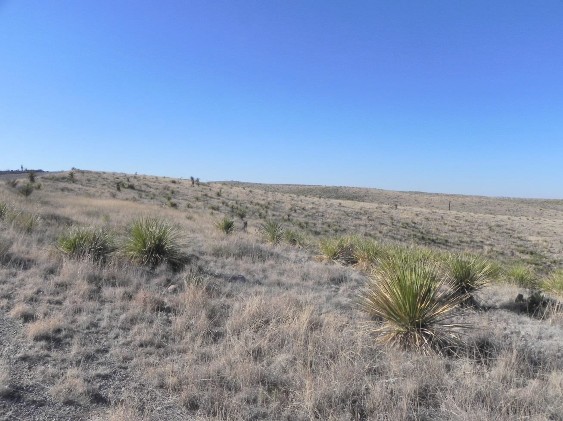
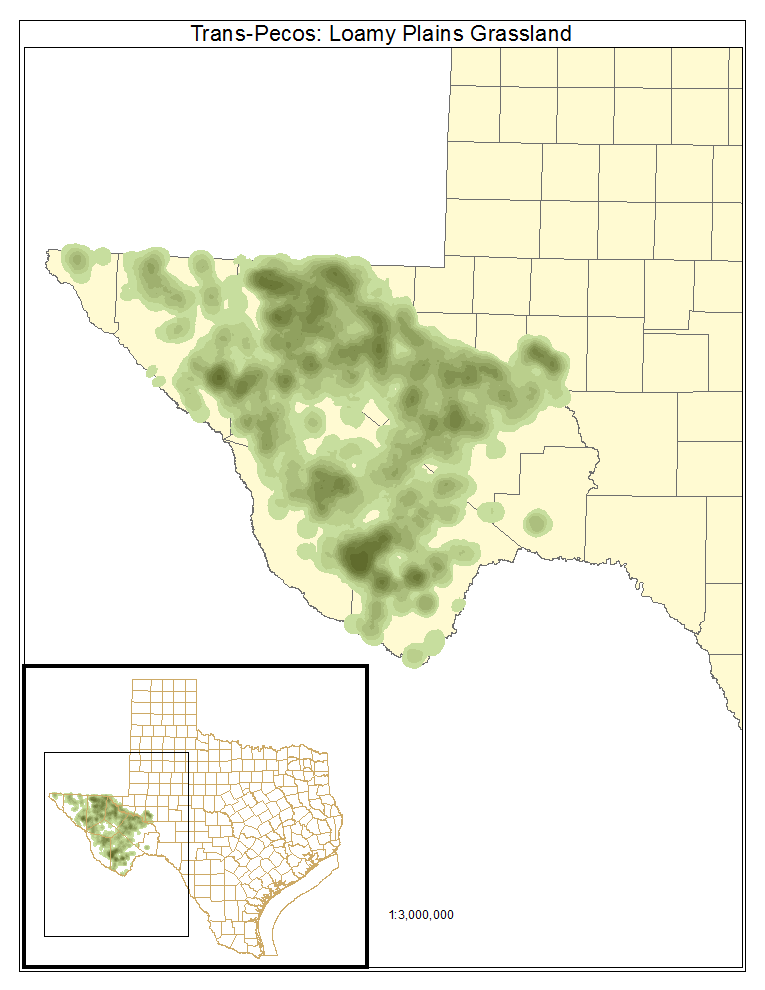
Trans-Pecos: Loamy Plains Grassland
This grassland occupies level, deep loams of intermountain basins and is frequently invaded by Prosopis glandulosa (honey mesquite), Larrea tridentata (creosotebush), and Flourensia cernua (tarbush).
Distribution Map
Photos

Public Land Occurrence
- Big Bend National Park: US National Park Service
- Big Bend Ranch State Park: Texas Parks & Wildlife Department
- Black Gap Wildlife Management Area: Texas Parks & Wildlife Department
- Davis Mountains State Park: Texas Parks & Wildlife Department
- Elephant Mountain Wildlife Management Area: Texas Parks & Wildlife Department
- Fort Davis National Historic Site: US National Park Service
- Guadalupe Mountains National Park: US National Park Service
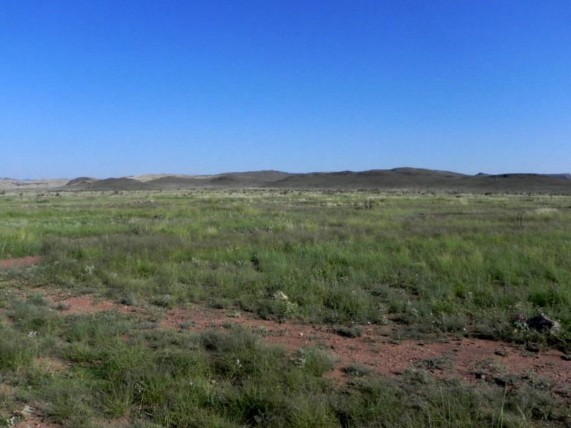
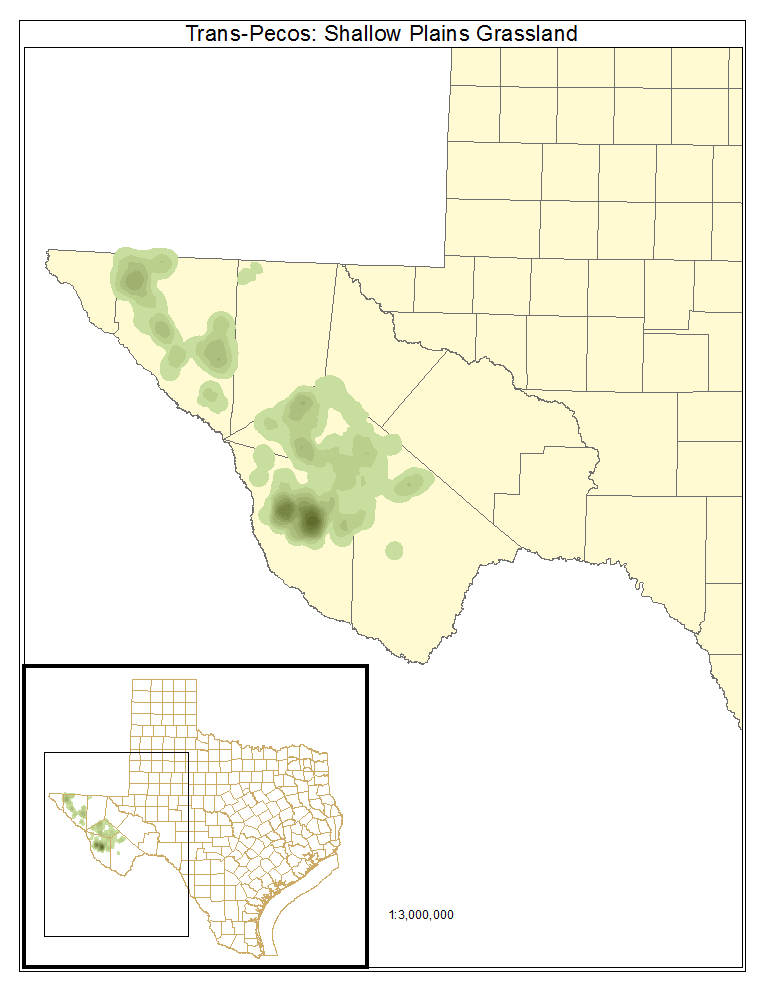
Trans-Pecos: Shallow Plains Grassland
This grassland occupies rolling uplands with shallow soils and is frequently invaded by Condalia ericoides (javelina bush), Juniperus spp. (junipers), and Acacia constricta (whitethorn acacia).
Distribution Map
Photos
