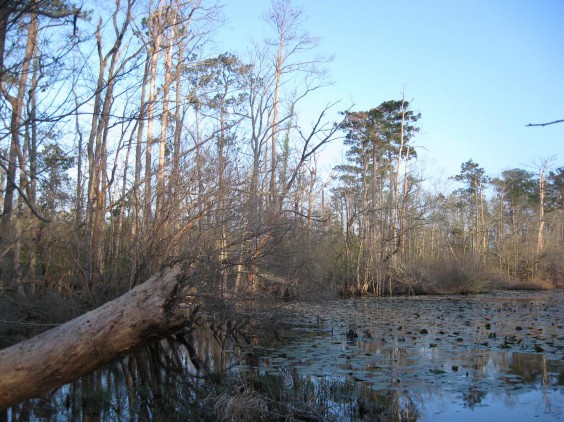
West Gulf Coastal Plain Flatwoods Pond
Geology
Pleistocene terraces, including the upper Beaumont Formation, but also mapped on the high Pleistocene terraces in the northern part of Texas. These are mapped as Quaternary Fluviatile Terrace (Tile) Deposits along the Red, Sulphur, and Sabine Rivers.
Landform
Occupy local topographic lows within the flatwoods.
Soils
Relatively fine-textured soils with an impermeable subsoil horizon, giving rise to a perched water table and saturated conditions during extended periods of the year.
Parent Description
The system as currently described, focuses on those herbaceous dominated wetlands that are embedded within the West Gulf Coastal Plain Longleaf Pine Wet Savanna and Flatwoods. As we mapped this system, it occupies sites with a much broader distribution, including wet, herbaceous dominated sites within the West Gulf Coastal Plain Wet Hardwood Flatwoods or West Gulf Coastal Plain Pine - Hardwood Flatwoods. This mapped system is likely dominated by species such as Panicum hemitomon (maidencane), Carex spp. (sedges), Rhynchospora (beaksedges), Eleocharis spp. (spikerushes), Andropogon glomeratus (bushy bluestem), and Ludwigia spp. (water-primroses). On drier sites Schizachyrium scoparium (little bluestem) may be present. Some sites may be dominated by the non-native Cynodon dactylon (bermudagrass). A few woody species may occur, including Nyssa biflora (swamp tupelo), Liquidambar styraciflua (sweetgum), Quercus nigra (water oak), Planera aquatica (water elm), and Cephalanthus occidentalis (common buttonbush). Flatwood ponds, as described by Bridges and Orzell, represent a more restricted subset of herbaceous-dominated sites with saturated soils resulting from perched water table due to an impermeable subsurface.
Ecological Mapping Systems
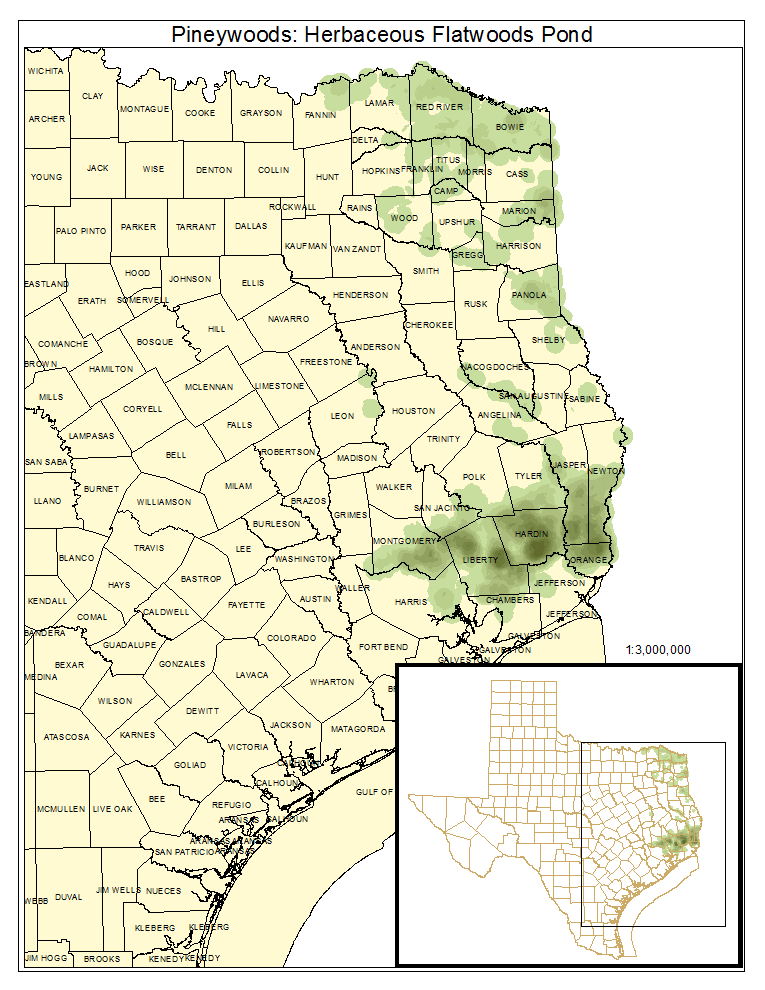
Pineywoods: Herbaceous Flatwoods Pond
As described for system.
Distribution Map
Photos
