- Trans Pecos
- High Plains/Panhandle
- Cross Timbers
- Hill Country
- Post Oak Savannah
- Pineywoods
- Oak Prairie
- South Texas Plains
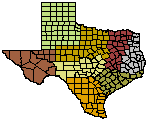
Wildlife Division District Map
Pineywoods Wildlife Management
Bobwhite Management
Habitat Management Recommendations
A primary quail management objective is to maintain or create the mosaic of small thickets of low growing woody brush throughout a ranch, as described above in woody cover requirements. Thickets of sumac, briers, plums, blackberries, etc. should be retained and encouraged to form. Although not as desirable, small clumps of low growing cedars could have some value as cover where other species do not grow or are in short supply. Where vines have grown up into a tree leaving ground too open to serve as quail cover, the tree can be cut half through a few feet above ground and pushed over, bringing the living vines closer to the ground. In the western portion of the area, the trunks of multi-stemmed mesquites can be half-cut and pushed over so that the limbs touch the ground but continue to grow, forming small areas protected from cattle grazing/deer browsing. Half-cutting mesquite should be done during the early and middle parts of the growing season, not during the dormant season. The individual "skeletons" of large cut cedars can also form small areas protected from grazing/browsing where patches of herbaceous and woody plants suitable for cover can become established. The number of browsing animals on the range (combination of wildlife and domestic livestock) needs to be maintained at a level where browsing pressure on low growing woody cover is not excessive.
Another objective is to improve the amount and quality of herbaceous cover. A well-planned deferred-rotation livestock grazing system (as described in the Livestock Recommendations section) can be used to create the patchy pattern of lightly grazed areas interspersed among more heavily grazed areas needed for nesting cover.
 Most
good seed producing forbs are early successional stage annuals that respond
to soil disturbance that sets back plant succession. Disking the soil is a
good practice that encourages the growth of forbs and other annual plants.
Disked strips should be long and meandering and 1 or 2 disc widths wide. The
same strips can be disked annually, or side-by-side strips can be disked on
an alternating basis every other year to create adjacent strips in various
stages of succession. The best plant response will occur in areas of deeper
sandy, sandy-loam soils. It is important that disced strips be located near
escape cover so they are useable by quail. Discing can be done anytime between
the first killing frost in the fall and the last frost in the spring, but
the optimum time is near the end of winter (January, February) shortly before
spring growth gets underway.
Most
good seed producing forbs are early successional stage annuals that respond
to soil disturbance that sets back plant succession. Disking the soil is a
good practice that encourages the growth of forbs and other annual plants.
Disked strips should be long and meandering and 1 or 2 disc widths wide. The
same strips can be disked annually, or side-by-side strips can be disked on
an alternating basis every other year to create adjacent strips in various
stages of succession. The best plant response will occur in areas of deeper
sandy, sandy-loam soils. It is important that disced strips be located near
escape cover so they are useable by quail. Discing can be done anytime between
the first killing frost in the fall and the last frost in the spring, but
the optimum time is near the end of winter (January, February) shortly before
spring growth gets underway.
Heavy spot grazing by cattle, such as occurs around salt blocks, feed areas, and water, causes soil disturbance that encourages forb growth. Salt blocks and feeding areas should be moved around the ranch to create small patches of disturbed ground.
Managing the habitat for the production of native food plants and cover should be the primary management goal. Supplemental feeding and/or the planting of food plots are not a substitute for good habitat management. These practices should only be considered as "supplements" to the native habitat, not as "cure-alls" for low quality and/or poorly managed habitats. Food plots and feeders alone will not increase the number of quail a range can support if the supplies of other required habitat elements such as cover are limited.
 Small
food plots of seed producing plants including but not limited to millets,
sorghum alum, and sorghum planted on deeper soils near cover can provide supplemental
food sources during periods of extreme weather conditions. A limiting factor
of supplemental food plots is sometimes an insufficient amount of rainfall
received in western east Texas during the summer. During dry years when the
production of native foods is limited and supplemental foods are most needed,
supplemental plantings will also be failures. During good years when the production
of native foods is adequate, supplemental plantings may do well, but are not
as necessary. Also, these seeds do not normally last long into the fall and
winter, due to normal fall rainfall. Another limiting factor is that most
types of supplemental plantings will have to be protected from livestock grazing
by fencing the plot or deferring the pasture.
Small
food plots of seed producing plants including but not limited to millets,
sorghum alum, and sorghum planted on deeper soils near cover can provide supplemental
food sources during periods of extreme weather conditions. A limiting factor
of supplemental food plots is sometimes an insufficient amount of rainfall
received in western east Texas during the summer. During dry years when the
production of native foods is limited and supplemental foods are most needed,
supplemental plantings will also be failures. During good years when the production
of native foods is adequate, supplemental plantings may do well, but are not
as necessary. Also, these seeds do not normally last long into the fall and
winter, due to normal fall rainfall. Another limiting factor is that most
types of supplemental plantings will have to be protected from livestock grazing
by fencing the plot or deferring the pasture.
Feeding can provide supplemental food during extreme weather conditions and help hold quail in an area. Broadcasting corn or sorghum by hand is one method of distributing supplemental feed. It can also be distributed from fixed feeders. An intensive feeding program would be one that provides 1 feeder per every 40 to 60 acres of quail habitat (feeders placed 440 to 540 yards apart in a grid pattern) so that every quail covey has access to several feeders. One feeder per 75 acres may be sufficient. As with all other types of food sources, feeders need to be located near escape and screening cover to be useable by quail. Some limitations of supplemental feeding are: they can be expensive and labor intensive, diseases and parasites can be spread at heavily used sites, predators learn to key on sites regularly used by quail, and, depending on the type of feeder used, they may have to be fenced from livestock.
 Prescribed
burning is a very effective, low-cost habitat management tool that can be
used to enhance plant diversity by stimulating production of a variety of
woody plants, forbs, and grasses. Burning can be used to remove rank stands
of herbaceous vegetation and plant litter that hinder quail movements. Also,
studies have shown that up to seven times more protein rich insects are present
in burned areas compared to unburned areas.
Prescribed
burning is a very effective, low-cost habitat management tool that can be
used to enhance plant diversity by stimulating production of a variety of
woody plants, forbs, and grasses. Burning can be used to remove rank stands
of herbaceous vegetation and plant litter that hinder quail movements. Also,
studies have shown that up to seven times more protein rich insects are present
in burned areas compared to unburned areas.
In summary, food and all the different types of cover must be available year around and suitably arranged to have a good quail habitat. The number of quail a range can produce and support will be dependent on the habitat element that is most limited. In other words, if cover is the limiting factor, increasing the amount of food beyond that needed for the number of quail that can be supported by the cover will not increase the range's quail carrying capacity, and vice versa.
See TPWD brochure 7000-37, Bobwhite Quail in Texas, Habitat Needs & Management Suggestions by A.S. Jackson, C. Holt, and D. W. Lay.
Notes: The same types of cover and seed producing forbs and supplemental food plants utilized by quail are also utilized by many other species of birds and mammals.
 (
(